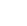
Thingy is a line of rapid prototyping platforms from Nordic Semiconductor. In this article, we will discuss the Nordic Thingy:53: a multi-sensor, multi-protocol wireless prototyping platform introduced this year.
It shares similarities with the Thingy:52 and Thingy:91 products from Nordic Semiconductor but has some brand-new features. At the core of it, you’ll find an nRF5340, the flagship dual-core wireless system-on-chip. It is one of the most powerful SoC to date among Nordic Semiconductor rapid prototyping platforms. In addition to having 1 MB of flash storage and 512 kB of RAM on the main application core, it also has a separate core for wireless connectivity. Both cores are Arm Cortex-M33, running at up to 128 and 64 MHz respectively. This gives the Thingy:53 capabilities never seen before in an application like this.
With the nRF21540 RF FEM adding range extension features and nPM1100 PMIC handling charging of the internal battery. The Thingy:53 feature three different types of IC from Nordic Semiconductor all at once. The Thingy:53 also features a wealth of different sensors. An environmental sensor measures the temperature, humidity, gas, and pressure surrounding the platform. This is useful in home automation or machine learning applications that alert the user or control other applications based on environmental conditions.
There is a magnetometer that can be used as a Hall effect sensor and a color and light sensor behind the clear plastic eye in the casing. The 6-axis inertial measurement unit can be used as a gyroscope and accelerometer to give an application awareness of the Thingy`s orientation and the additional low-power accelerometer and the MEMS microphone have the ability to wake the nRF5340 from sleep allowing for creating ultra-low-power applications that only run the nRF5340 when there are actual inputs to process. All these sensors can be taken advantage of when collecting data for or running inferencing on embedded ML models directly on the Thingy:53. The processing power and memory size of the nRF5340 SoC inside the Thingy:53 allows it to run ML models.
The internal layout of the Thingy:53 (Source: Nordic Semiconductor)
A mobile app is developed for seamlessly integrating the Thingy:53 with Edge Impulse studio entirely wirelessly over Bluetooth LE. You can collect data and wirelessly transfer them to the cloud, train your model in Edge Impulse`s Cloud and then transfer it, wirelessly of course, back to the Thingy for deployment and inferencing, using the app as a GUI. The Thingy:53 comes pre-installed with firmware to work with the nRF Edge Impulse app but if you want to replace the firmware on the Thingy, this also can be done completely wirelessly through the nRF Programmer app.
Example of Edge Impulse (Source: Nordic Semiconductor)
There is some quality of life improvement to the physical design of the Thingy:53. It is added that handy little flap on the bottom of the casing to allow direct access to the power switch and all external connections of the Thingy. It is also added a 4-pin JST connector that’s compatible with standards like Qwiic, Groove and Stemma to allow easy integration with external accessories. This little slot is for debug and current measurement board that is delivered with every Thingy:53. This allows you to access debug and current measurement pins on the Thingy`s SoC and PMIC to make debugging and power profiling with external tools much easier.